Train a Model
This tutorial will guide you through the process of training a model using DashAI.
Prerequisites
Before starting, make sure you have:
A dataset uploaded to DashAI
Understanding of your dataset’s columns (features and target)
Step-by-Step Guide
1. Access the Experiments Section
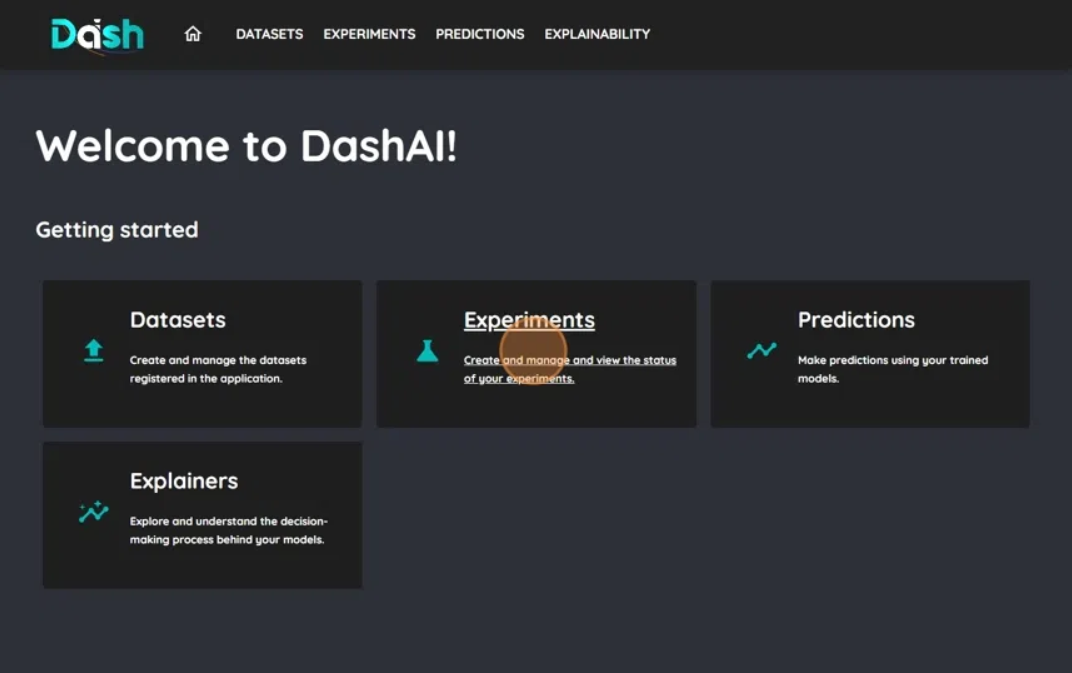
Click on the “Experiments” button in the navigation bar to access the experiments interface.
2. Create New Experiment
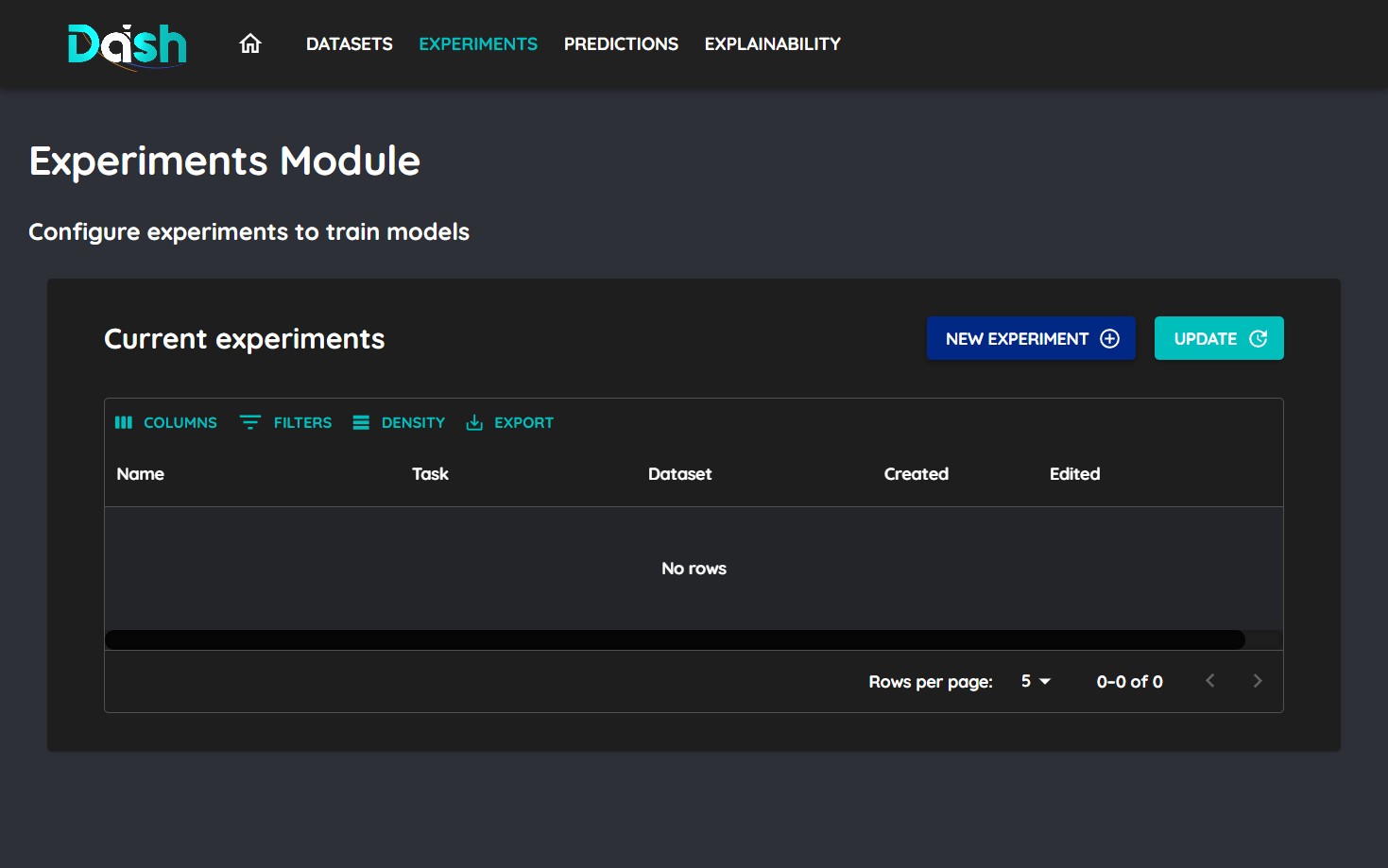
Click on the “New Experiment” button to start creating your experiment.
3. Select Task and Set Name
Write a name for your experiment
- Select the appropriate task type for your problem:
Text Classification
Tabular Classification
Image Classification
Regression
Translation
Click “Next” to proceed
4. Select Dataset
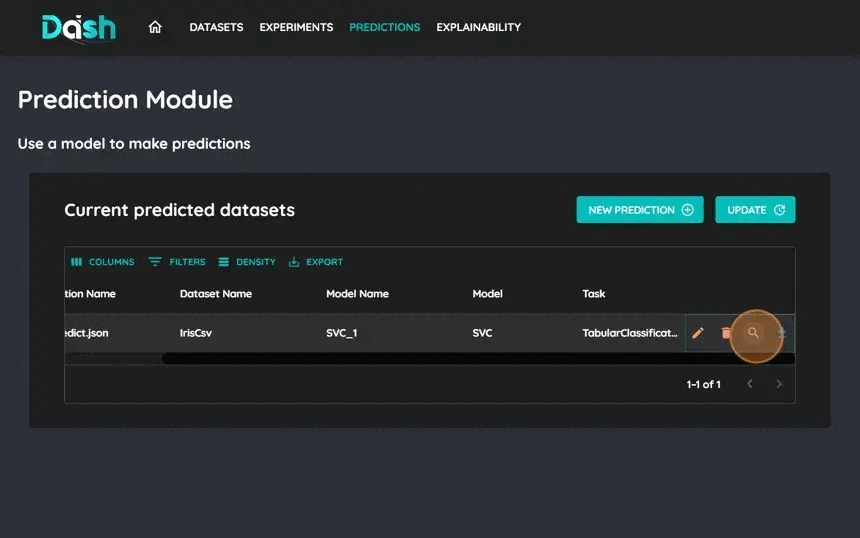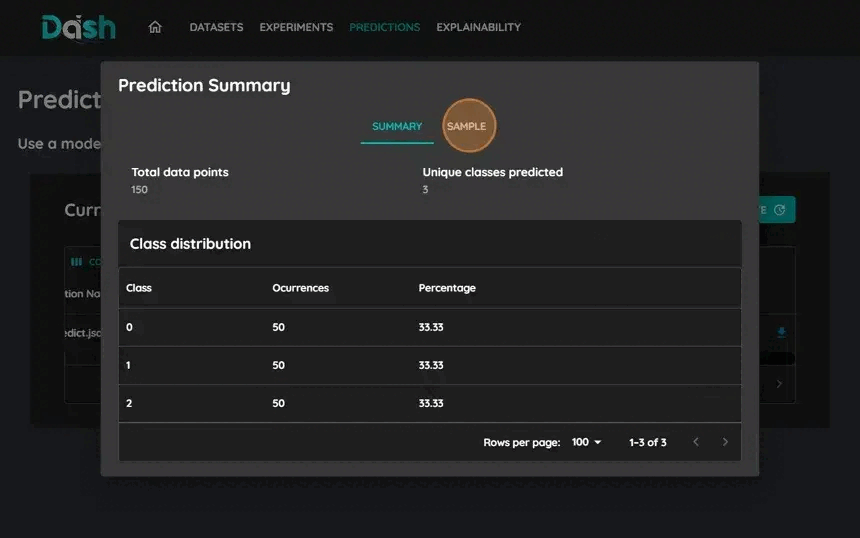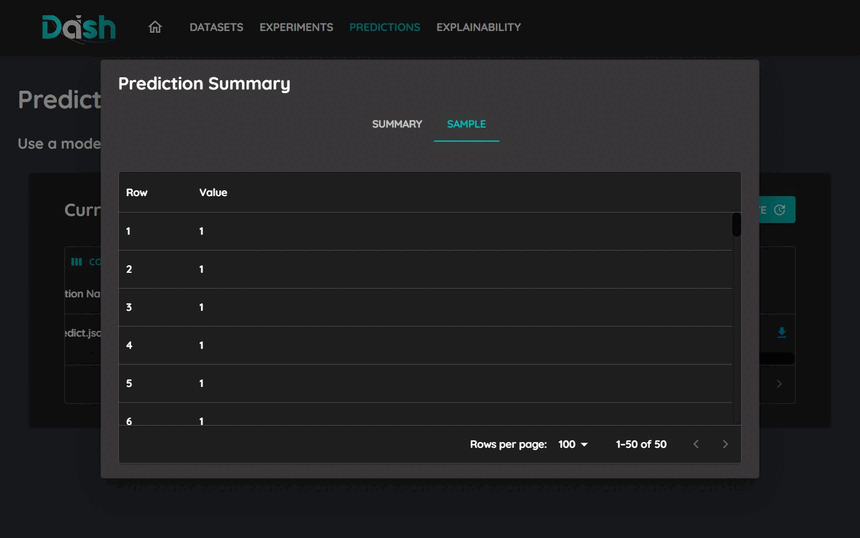
Choose the dataset you want to use for training
Click “Next” to proceed
5. Configure Input/Output and Splits
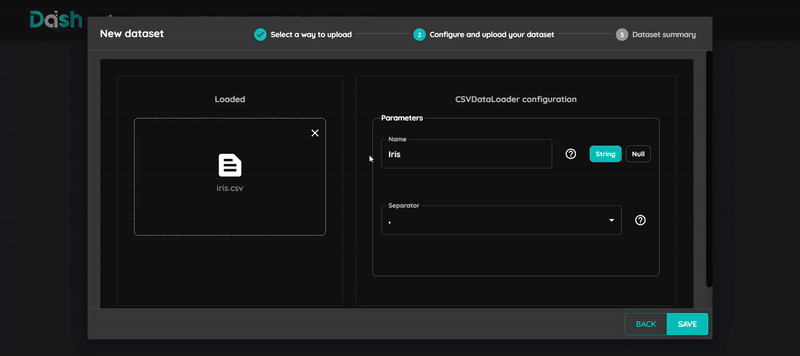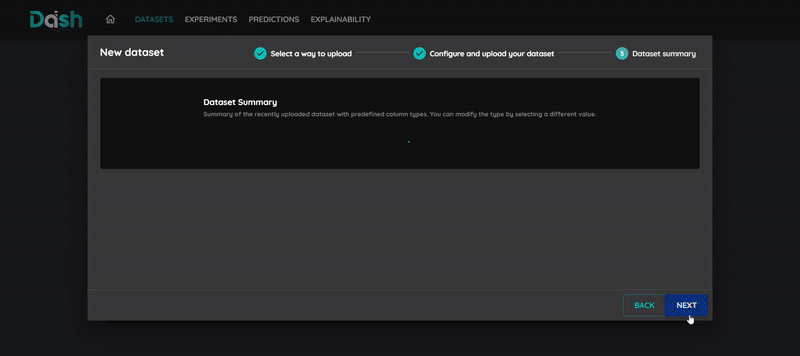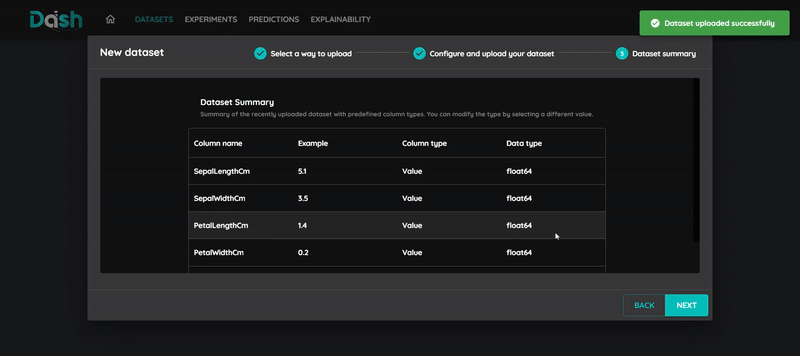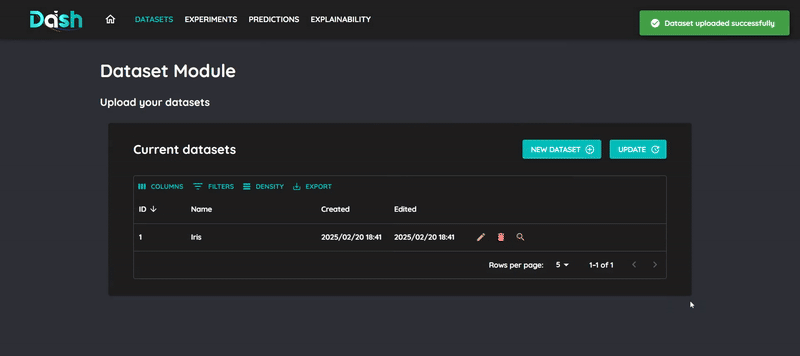
Select the input columns (features)
Select the output column (target)
Configure the train/test/validation splits
Click “Next” to proceed
6. Select and Configure Model
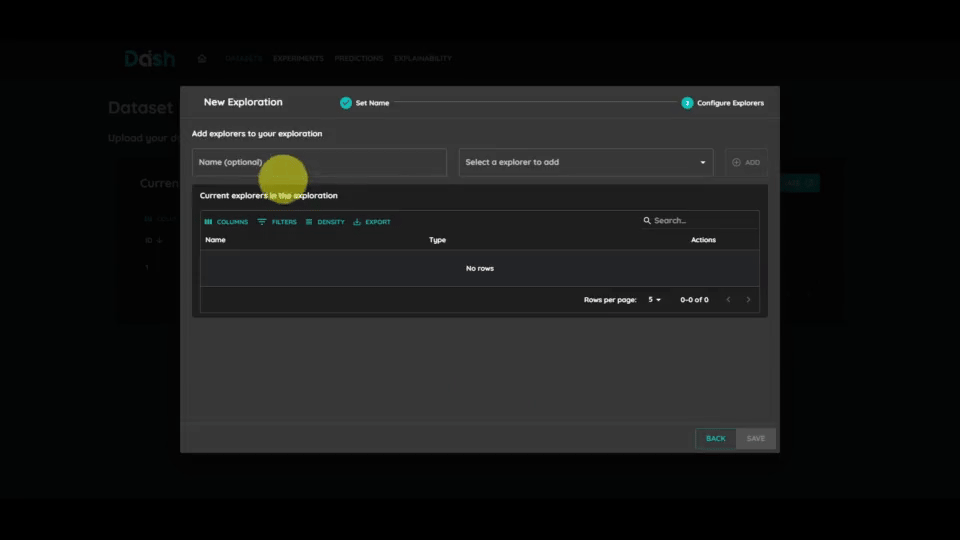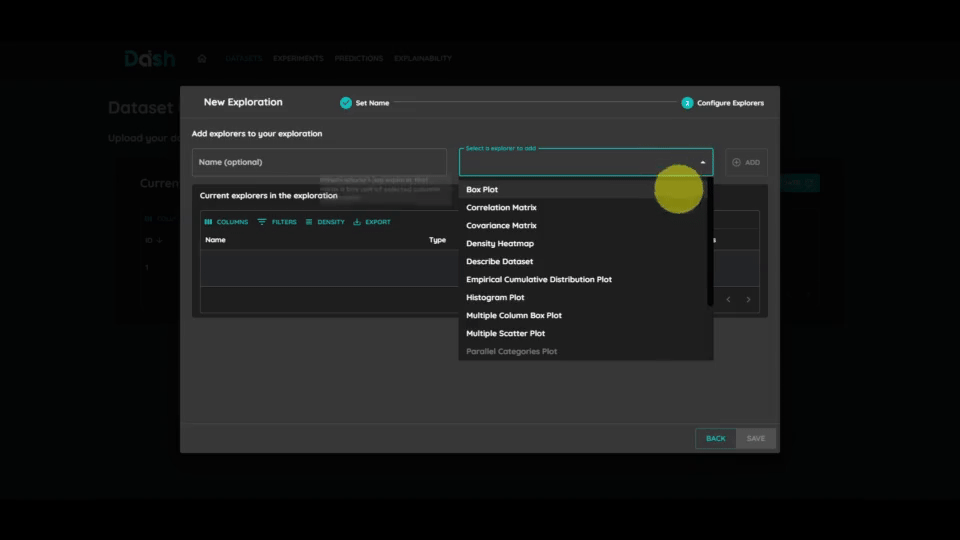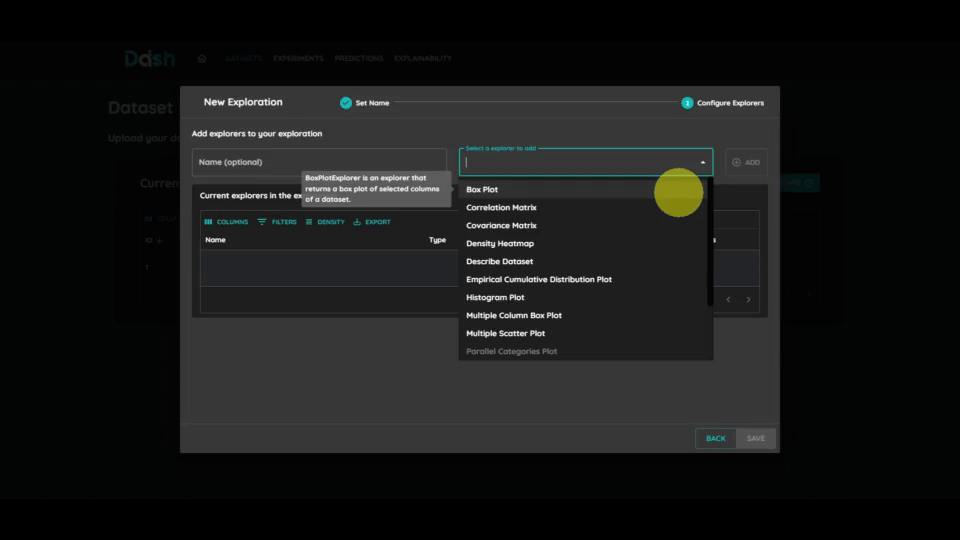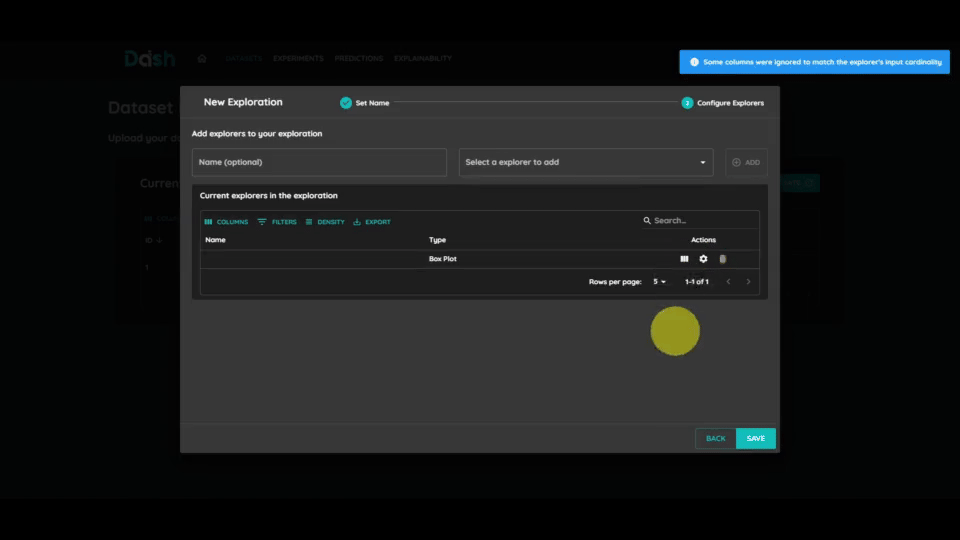
You can select multiple models to train and compare their performance. For each model:
Click on the “Select a model to add” button
Choose a model suitable for your task
Configure the model parameters
Repeat to add more models
Here are some recommended model combinations for each task type:
- For Text Classification:
DistilBERT + Bag of Words: Compare simple vs advanced approaches
Multiple DistilBERT instances with different parameters
- For Tabular Classification:
Random Forest + Logistic Regression: Compare linear vs non-linear methods
SVC + Random Forest: Compare different algorithmic approaches
- For Image Classification:
Different ViT configurations to compare performance
- For Regression:
Linear Regression + Random Forest: Compare simple vs complex relationships
Multiple SVR instances with different kernels
Note
Training multiple models allows you to:
Compare performance across different architectures
Find the best model for your specific dataset
Understand trade-offs between complexity and performance
Experiment with different hyperparameter configurations
For a complete list of available models and their detailed documentation, see Models.
7. Model Optimization
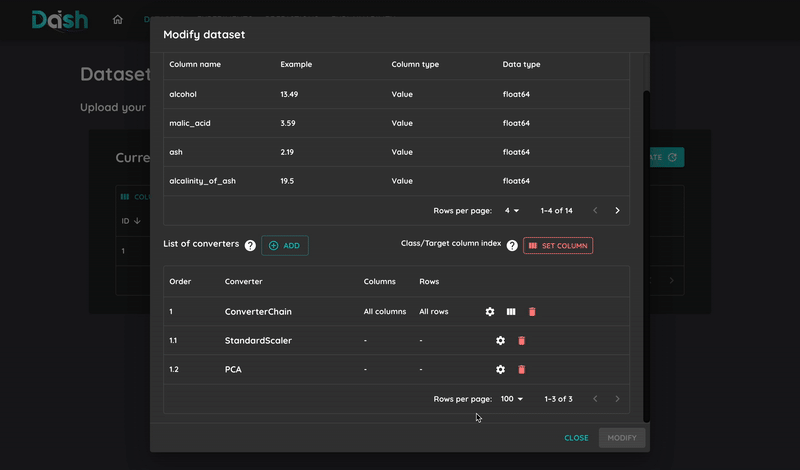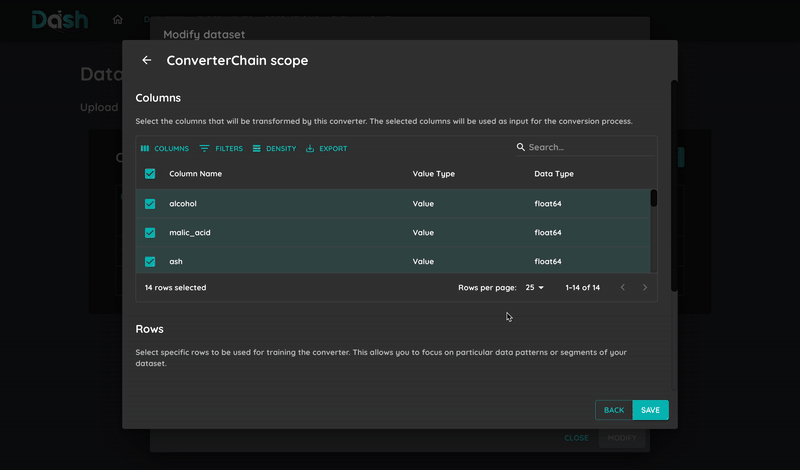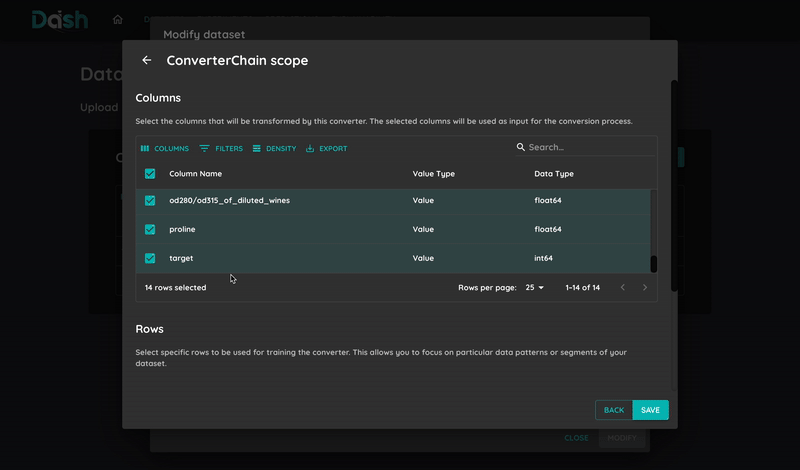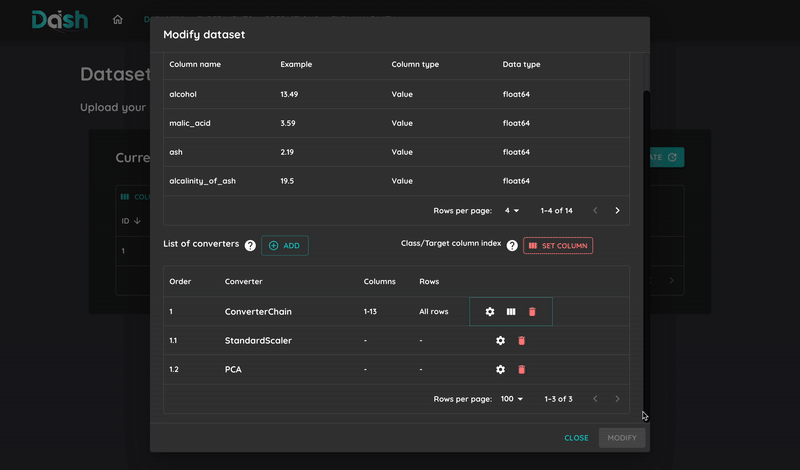
DashAI provides automatic model optimization through:
- Hyperparameter Optimization: Find the best parameters for your model automatically
Each parameter combination is evaluated using the selected optimization metric
- Example parameters to optimize:
SVC: Regularization parameter (C)
Random Forest: Number of trees, maximum depth
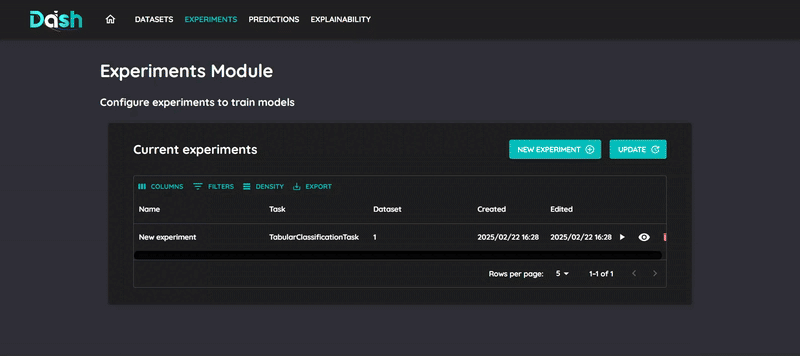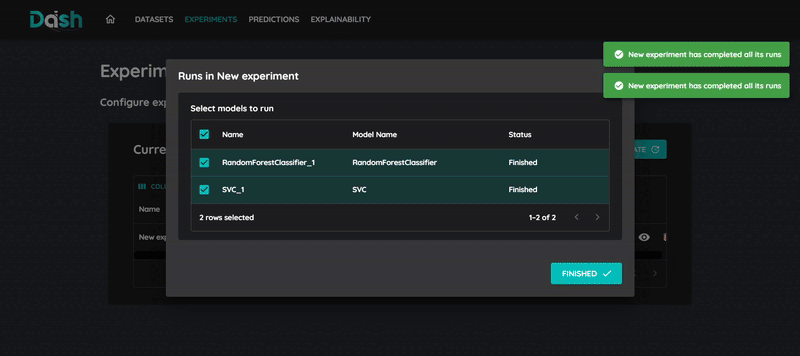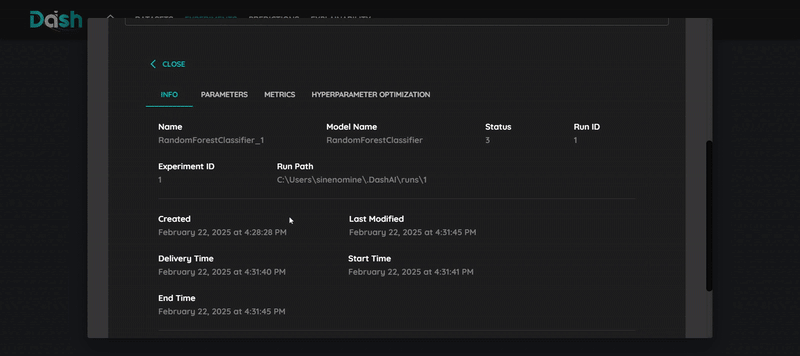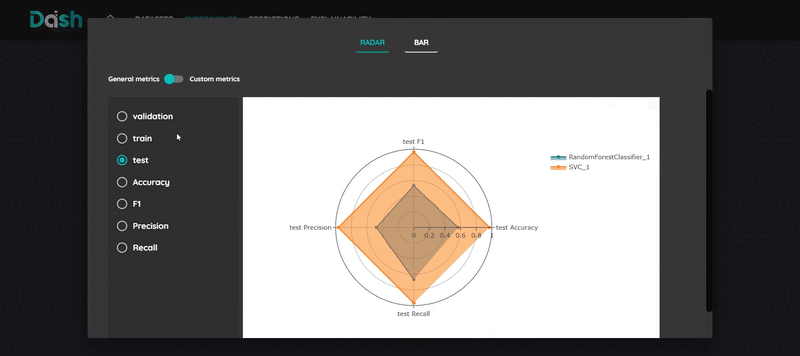
- Optimization Metrics: The metric used to compare different parameter combinations
- Classification:
Accuracy: Overall correctness
F1-score: Balance between precision and recall
Precision: Exactness of positive predictions
Recall: Completeness of positive predictions
- Regression:
Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE): Root mean squared error
Mean Absolute Error (MAE): Mean absolute error
- Translation:
BLEU: Similarity between translations
TER: Translation edit rate
- Optimizers: Algorithms that guide the hyperparameter search
OptunaOptimizer: Efficient parameter search using Bayesian optimization
HyperOptOptimizer: Tree-structured Parzen Estimators for parameter search
Note
The optimization process will: 1. Try different parameter combinations 2. Evaluate each combination using the selected metric 3. Keep the parameters that achieve the best metric value
8. Train and review results
To train your models:
Click “Start” to start the training process
Wait for training completion
Review the model’s performance metrics
Compare with other runs
Tips and Best Practices
Start with a small dataset to test your configuration
Try different model architectures for your task
Use appropriate evaluation metrics for your problem
Save successful model configurations for future use
Consider using model optimization for better results
Troubleshooting
- If training fails, check:
Dataset format and preprocessing
Model parameter values
System resources (memory, GPU)
- For poor performance:
Review feature selection
Adjust model hyperparameters
Consider data preprocessing
Try different model architectures